Valve Body Machining Process
Publish Time: Author: Site Editor Visit: 8574
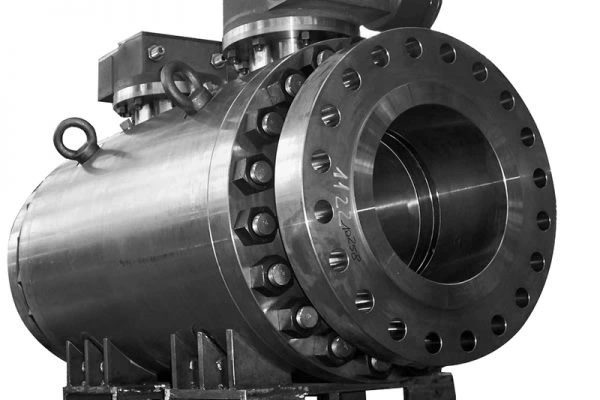
The valve body machining process involves the use of various machining techniques to create the necessary features and dimensions on the valve body to achieve the desired performance. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Material selection: The first step in the valve body machining process is to select the appropriate material for the valve body. The material chosen will depend on various factors, such as the operating conditions, pressure, temperature, and the desired durability of the valve. Commonly used materials for valve bodies include metals, such as cast iron, steel, and brass, as well as plastics and composites.
- Design and engineering: Once the material has been selected, the valve body design is created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This step involves defining the size, shape, and features of the valve body, as well as the location of the ports and other machining features.
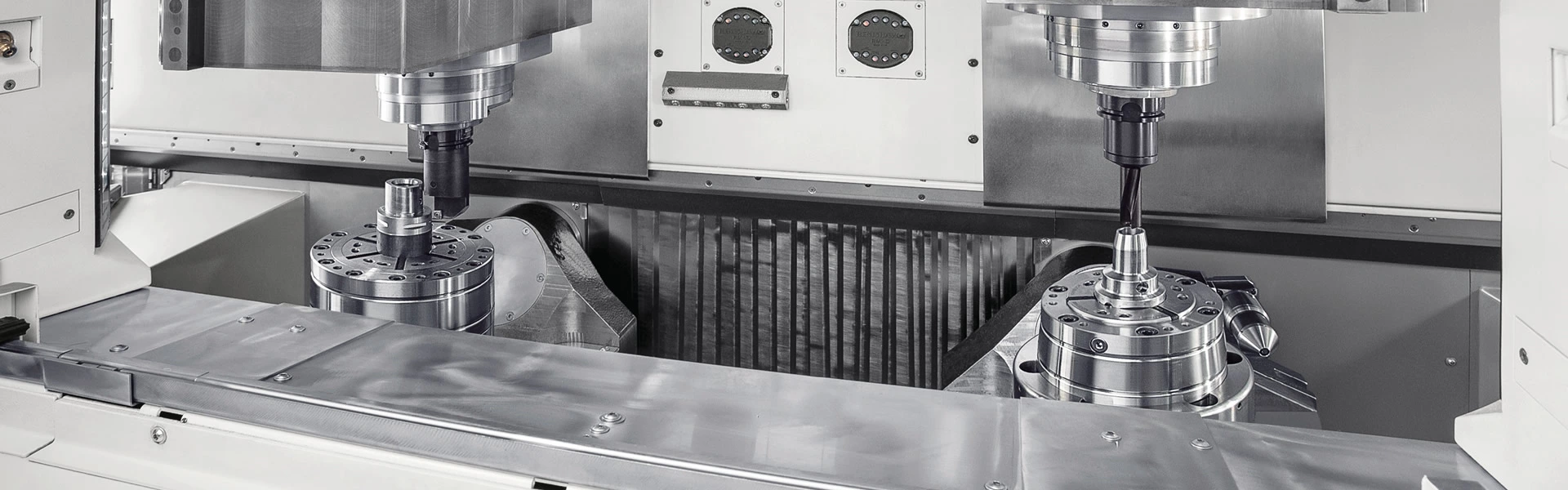
- Tooling: To machine the valve body, specialized tools and equipment are required. These tools are typically created using CNC machines or other advanced manufacturing techniques. The tooling includes the cutting tools, such as drills, mills, and taps, as well as the fixtures and holding devices that hold the valve body in place during the machining process.
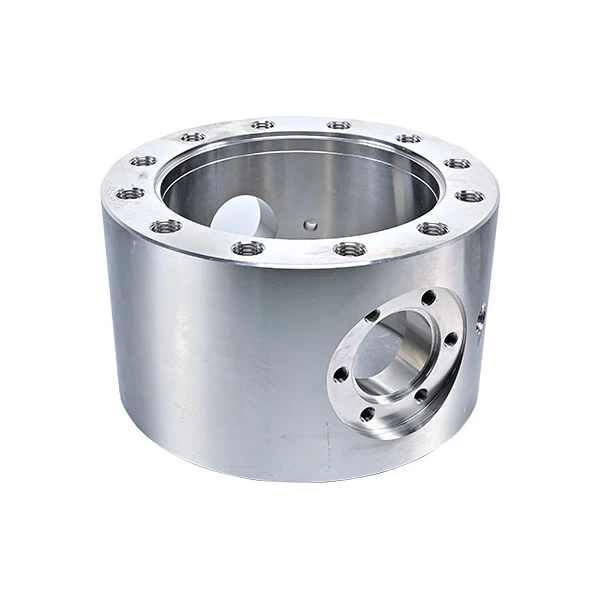
- Machining: The actual machining process involves using the cutting tools to remove material from the valve body and create the desired features. This may involve drilling holes for the ports, cutting grooves for the trim and positioning systems, and creating threads for the fasteners.
- Finishing: Once the basic machining has been completed, the valve body will need to be finished to achieve the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy. This may involve using additional machining techniques, such as grinding, honing, or polishing, to achieve the desired results.
- Inspection: Before the valve body is assembled, it must be inspected to ensure that it meets the required specifications and tolerances. This may involve using measuring instruments, such as micrometers and calipers, to check the dimensions and surface finish of the valve body.